Category

BLDC Motor Supplier
Home » BLDC Motor Application » 54V Brushless DC Motor for Current Server
54V Brushless DC Motor for Current Server
What is the cloud computing? Cloud computing refers to a set of remote servers, which store and migrate data in different parts of the world for the convenience of accessing these data via Wi-Fi, LAN or cellular network. These remote servers play the role of large-scale storage equipment, and equipment of the kind is usually made up of the server group in the warehouse or the server field. The server field requires a constant environment temperature to operate at the highest performance and to minimize the probability of faults.
In the real life, servers use a series of fans to cool down the electronic components. Just as many of us have experienced, the temperature of the electronic equipment might easily increase, thus finally impairing its maximum performance. In order to maximally reduce the cost and dimensions of radiators, the BLDC motor should be used to cool down the electronic equipment via the air flow. The environmental temperature can be made use for heating, and the temperature can maintain constant through heating ventilation air-conditioner (HVAC) so as to cool down electronic modules in the server frame.
Traditionally, the server adopts the 12V BLDC motor fan to cool down the electronic equipment in the refrigerator. However, just like the automobile application, the 54V BLDC motor is also applicable to the server for several reasons. This article mainly discusses two major reasons why the server manufacturer adopts the 54V BLDC motor rather than the traditional 12V BLDC electric motor.
Two reasons for switching to 54V BLDC motor
Reason one: The server manufacturer is using 54V BLDC motor rather than the traditional 12V one first because the former just uses one fourth of the current. In this way, the electric motor manufacturer can adopt thinner copper wire. Meanwhile, the electric motor can be made smaller, and fewer raw materials are required to launch the same working load, thus cutting the overall cost of electric motor manufacturing. Second, by using 54v BLDC electric motor, the server manufacturer can cut the cost of expensive cables. Compared with the 12V BLDC motor using the same power source bus cable, the 54V BLDC motor can increase the number of electric motors for power supply by four folds. When the power is the same, the high-voltage electric motor can adopt a smaller cable and a narrower PCB track width.
For example, in the 450W server, the power consumption of the 12V BLDC motor fan is 32W. The current required by their power supply can be briefly calculated through the power equations.
Assume that the power requirement of the 54V BLDC fan is the same, the current required can be reduced to around 0.67A. In this way, the server engineer can adopt the 26 AWG wire rather than the 20 AWG wire.
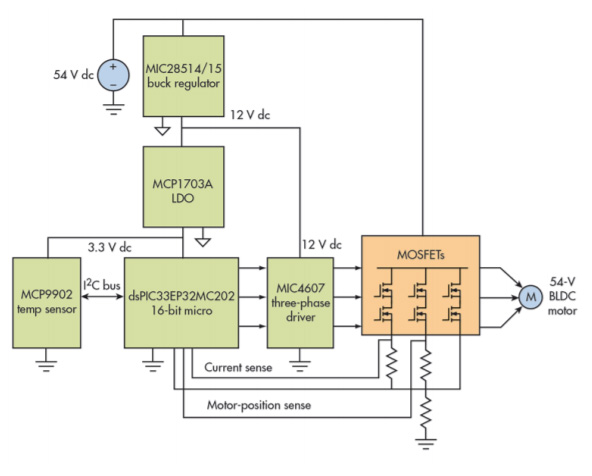 In terms of the PCB track width, the 54 BLDC fan is adopted. The server engineer can use the 0.012 inch PCB track width. On the contrary, when the 12V BLDC motor fan is adopted, the PCB track width reaches 0.1 inch. When you need to add the power source bus to the server system, this can greatly save the circuit board area occupied thereby.
In terms of the PCB track width, the 54 BLDC fan is adopted. The server engineer can use the 0.012 inch PCB track width. On the contrary, when the 12V BLDC motor fan is adopted, the PCB track width reaches 0.1 inch. When you need to add the power source bus to the server system, this can greatly save the circuit board area occupied thereby.
Reason two: Another advantage for the server manufacturer's adoption of the 54V BLDC motor is that the electric motor can operate at a faster speed, thus driving more air density. At the same time, the external dimensions of the electric motor are still the same to those of the 12V BLDC motor. To the end, the extra current should be input to support the torque force of the electric motor to meet the power requirements.
For example, the server manufacturer can use 50W BLDC motor rather than the traditional 32W motor to realize a larger air flow. When the 54V BLDC motor is adopted, the current required by the working load is just 0.93A, which is far smaller than 4.17A, the current required by the 12V BLDC motor electric motor to drive the 50W electric motor to achieve the same work load. Most importantly, 12V BLDC motor needs a larger PCB rooting and a larger cable, which will undoubtedly increase the overall cost. The server manufacturer adopting the 54V bus voltage can operate the fan at a faster speed to increase the air flow density while reducing the labeling cost at the same time.
In the real life, servers use a series of fans to cool down the electronic components. Just as many of us have experienced, the temperature of the electronic equipment might easily increase, thus finally impairing its maximum performance. In order to maximally reduce the cost and dimensions of radiators, the BLDC motor should be used to cool down the electronic equipment via the air flow. The environmental temperature can be made use for heating, and the temperature can maintain constant through heating ventilation air-conditioner (HVAC) so as to cool down electronic modules in the server frame.
Traditionally, the server adopts the 12V BLDC motor fan to cool down the electronic equipment in the refrigerator. However, just like the automobile application, the 54V BLDC motor is also applicable to the server for several reasons. This article mainly discusses two major reasons why the server manufacturer adopts the 54V BLDC motor rather than the traditional 12V BLDC electric motor.
Two reasons for switching to 54V BLDC motor
Reason one: The server manufacturer is using 54V BLDC motor rather than the traditional 12V one first because the former just uses one fourth of the current. In this way, the electric motor manufacturer can adopt thinner copper wire. Meanwhile, the electric motor can be made smaller, and fewer raw materials are required to launch the same working load, thus cutting the overall cost of electric motor manufacturing. Second, by using 54v BLDC electric motor, the server manufacturer can cut the cost of expensive cables. Compared with the 12V BLDC motor using the same power source bus cable, the 54V BLDC motor can increase the number of electric motors for power supply by four folds. When the power is the same, the high-voltage electric motor can adopt a smaller cable and a narrower PCB track width.
For example, in the 450W server, the power consumption of the 12V BLDC motor fan is 32W. The current required by their power supply can be briefly calculated through the power equations.
Assume that the power requirement of the 54V BLDC fan is the same, the current required can be reduced to around 0.67A. In this way, the server engineer can adopt the 26 AWG wire rather than the 20 AWG wire.

Reason two: Another advantage for the server manufacturer's adoption of the 54V BLDC motor is that the electric motor can operate at a faster speed, thus driving more air density. At the same time, the external dimensions of the electric motor are still the same to those of the 12V BLDC motor. To the end, the extra current should be input to support the torque force of the electric motor to meet the power requirements.
For example, the server manufacturer can use 50W BLDC motor rather than the traditional 32W motor to realize a larger air flow. When the 54V BLDC motor is adopted, the current required by the working load is just 0.93A, which is far smaller than 4.17A, the current required by the 12V BLDC motor electric motor to drive the 50W electric motor to achieve the same work load. Most importantly, 12V BLDC motor needs a larger PCB rooting and a larger cable, which will undoubtedly increase the overall cost. The server manufacturer adopting the 54V bus voltage can operate the fan at a faster speed to increase the air flow density while reducing the labeling cost at the same time.
Post a Comment:
You may also like: